Updates Of Codex Activities In Bhutan
"Safe Food, Strong Standards, Global Trust: Bhutan’s Codex Commitment in Action!"
Nationaal CODEX Procedural Manual
- Contribute towards strengthening Bhutan’s national food control systems.
- Effectively manage the works of Codex in Bhutan; and
- Actively participate in the elaboration of international food standards to play a meaningful role as a member of the CAC.
- Section I details the Codex structures in Bhutan along with their key roles and responsibilities. Section II outlines working procedures for Codex Committees, towards efficient and smooth operation of National Codex Committee and Codex sub-committee (s) of Bhutan to:
- formulate mandatory Food Standards (Technical Regulations) and
- formulate national positions on Codex Works.
- Section III defines the procedure for selection of the Leader and Members of Bhutanese delegation for participation to Codex meetings.
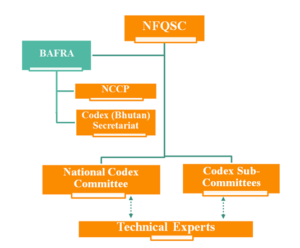
CODEX Structure in Bhutan
- National Food Quality and Safety Commission (NFQSC): Highest decision-making body on food quality and safety.
- Bhutan Agriculture and Food Regulatory Authority (BAFRA)
- Head of BAFRA is the National Codex Contact Point (NCCP)
- Bhutan (Codex) Secretariat is established in BAFRA to manage the works of Codex in Bhutan.
- National Codex Committee (NCC): Comprises of national experts from relevant agencies to provide technical opinion on food safety, quality and standards.
- Codex Sub-committee (s): Comprises of national technical experts to assist works of NCC and function as shadow committees to Codex Committees of CAC.
National Food Quality And Safety Commission
- Development and acceptance of national Technical Regulations (mandatory food Standards) regarding food quality, food safety, ingredients, additives, adulterated food, weights and measures, laboratories and other technical issues.
- Preparation of standards, rules and regulations, orders, and notices under the Food Act of Bhutan 2005.
- Policy decisions related to all Codex activities and issues.
National CODEX Committee And Sub-Committees
Formulation of Food Technical Regulations

CODEX Coordinating Committee for Asia (CCASIA)
CODEX Alimentarius Commission
ABOUT CODEX
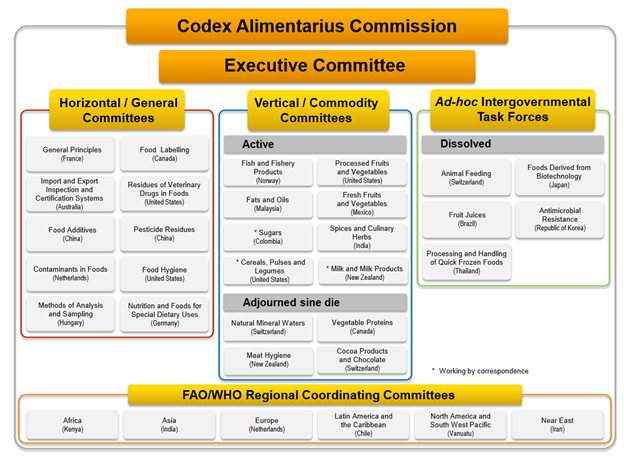
CODEX COMMITTEES
The Executive Committee acts on behalf of the Commission as its executive organ and assists in the management of its programme of standards development, mainly by conducting a critical review of its work programme, making proposals regarding general orientation and strategic planning.
- Committees, which prepare draft standards for submission to the Commission; may be either General Subject or Commodity specific
- Coordinating Committees , through which regions or groups of countries coordinate food standards activities in the region, including the development of regional standards. Currently there are six Codex regions.
- Task Forces , ad hoc Intergovernmental Task force with very limited terms of reference established for a fixed period of time.
Task Force on Antimicrobial Resistance with an objective of developing guidance on the management of foodborne antimicrobial resistance is currently active.
CODEX TEXTS
“Voluntary in nature, Codex standards can be general or specific and are recognized by WTO Agreements as reference standards”
General Standards, Guidelines and Codes of Practice
Commodity standards
Codex commodity standards refer to a specific product although increasingly Codex now develops standards for food groups.
Regional standards
Standards developed by the respective Regional Coordinating Committees, applicable to the respective regions.
The list of adopted standards and other texts can be available here
Bhutan Food and Drug Authority
- Ministry of Health,
- Kawajangsa,
- Tashichhodzong, Thimphu
- Toll Free No: 1555
- Post box : 1071
- Email: bfdahq@bfda.gov.bt